Rails에서 form 생성시 parameter 관련 문제
05 Feb 2016<h5>Parameter 전송시 나타날 수 있는 문제 3가지</h5>
<ol>
<li>token과 관련된 문제(unexpected token)</li>
<li>Strong parameter</li>
<li>DB와 Schema.rb 불일치 문제</li>
</ol>웹 어플리케이션에서 데이터 입력 form을 만들어서 데이터를 저장하는 작업은 매우 일반적인 작업입니다. 그리고 사용자가 입력한 데이터는 parameters를 이용해서 저장됩니다. Rails도 당연히 이 방식을 따릅니다. 다만 parameter를 넘겨주는 방식이 다른 프레임워크와 다른 면이 있어서, MVC 기반의 프레임워크에서 일반적으로 사용하는 방법으로는 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
이 포스팅에서는 내가 form을 잘 만들었다고 생각하고, parameter를 넘겼는데 생길 수 있는 문제 중 흔히 보이는 3가지 문제들과 그 해결방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
1. token과 관련된 문제(unexpected token)
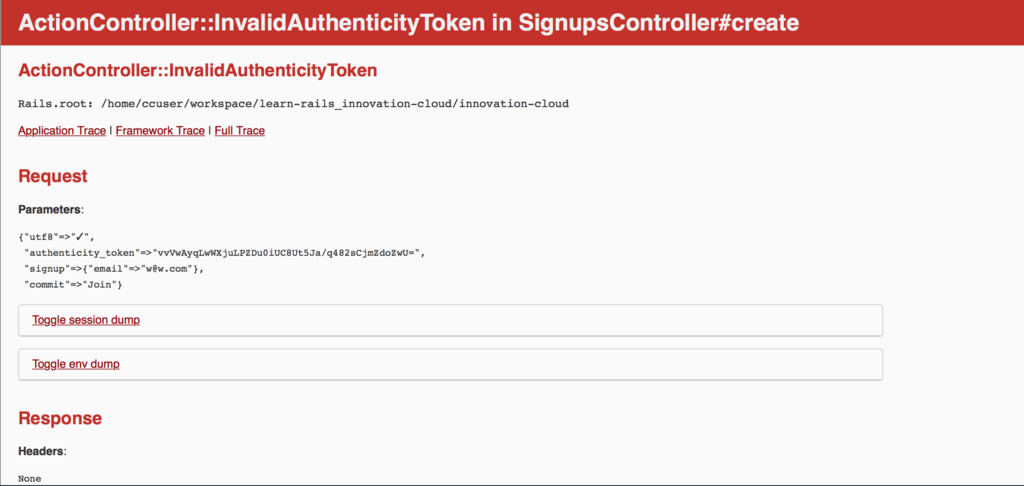
이 오류는 아직 rails에 익숙하지 않아서 rails form을 사용하지 않고, html 태그를 사용하는 분들이 흔히 보는 오류 메세지입니다.(사실 저도 아직 잘 못 씁니다..) Rails에서는 기본적으로 입력 form을 생성할 때 보안을 강화하기 위해 문자열 인코딩 정보와 token이라는 일종의 암호문을 함께 전송합니다. 그런데 이 두가지는 rails에서 제공하는 form helper로 전송할 때는 자동으로 생성되지만, html태그로 전송될 때는 자동으로 생성되지 않습니다.
간단한 예시로 무엇이 문제인지 알아보겠습니다.
<%= form_tag do %>
Form contents
<% end %> Rails는 기본적으로 html에서 사용하는 form 이외에 자신들만의 form을 가지고 있습니다. 위에서 보는 <%= form_tag do %>가 대표적인 예시입니다. 위의 form은 아무 input이 없는 form처럼 보이지만 사실 rails form은 기본적으로 인코딩 정보와 token을 보이지 않게 같이 전송합니다. 그래서 위의 form은 실제로는 아래와 같은 form을 만듭니다.
#app/views/posts.html.erb
<form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/" method="post">
<input name="utf8" type="hidden" value="✓" />
<input name="authenticity_token" type="hidden" value="J7CBxfHalt49OSHp27hblqK20c9PgwJ108nDHX/8Cts=" />
Form contents
</form>굳이 인코딩 정보와 token을 넣는 이유는 보안을 강화하기 위해서입니다.
해결방법
해결방법은 간단합니다.
- rails form을 익히고, 사용하기(권장)
- application_controller 수정하기
1. Rails form을 익히고, 사용하기(권장)
먼저 rails form을 잘 익히고 사용하는 방법이 가장 좋습니다. 굳이 강화된 보안을 무시하면서 html태그를 사용할 필요는 없다고 생각합니다. Rails form_tag 관련 문서 앞의 링크의 문서처럼 rails form tag과 html form tag를 잘 비교하면서 설명한 문서가 있습니다. rails를 더 잘 쓰시려면 배우는 것이 필수입니다. 익숙해지면 html tag보다 더 편리합니다.
2. Application_controller 수정하기
다음 방법은 권장하지는 않는 방법입니다만, 보안 체크를 꺼버리는 방법이 있습니다.app/controllers/application_controller.rb에 가보시면 다음과 같은 코드가 기본적으로 설정되어 있습니다.
class ApplicationController < ActionController::Base
# Prevent CSRF attacks by raising an exception.
# For APIs, you may want to use :null_session instead.
protect_from_forgery with: :exception
end 여기서 4번째 줄의 protect_from_forgery with: :exception부분을 주석처리해주면 token관련 오류는 보지 않을 수 있습니다. 하지만 거듭 강조하지만 보안도 개발자가 고려해야 하는 것중 하나이기 때문에, 이는 권장하지 않는 방법입니다. 구글에 rails form 관련 문서를 꼭 읽어보세요.
2. Strong parameter
strong parameter 문제는 scaffold로 app을 만들었을 때 흔히 나오는 문제입니다. 다음은 scaffold로 post를 만들었을 때의 post controller입니다.
#app/controllers/posts_controller.rb
class PostsController < ApplicationController
before_action :set_post, only: [:show, :edit, :update, :destroy]
def index
@posts = Post.all
end
def show
end
def new
@post = Post.new
end
def edit
end
def create
@post = Post.new(post_params)
respond_to do |format|
if @post.save
format.html { redirect_to @post, notice: 'Post was successfully created.' }
format.json { render :show, status: :created, location: @post }
else
format.html { render :new }
format.json { render json: @post.errors, status: :unprocessable_entity }
end
end
end
def update
respond_to do |format|
if @post.update(post_params)
format.html { redirect_to @post, notice: 'Post was successfully updated.' }
format.json { render :show, status: :ok, location: @post }
else
format.html { render :edit }
format.json { render json: @post.errors, status: :unprocessable_entity }
end
end
end
def destroy
@post.destroy
respond_to do |format|
format.html { redirect_to posts_url, notice: 'Post was successfully destroyed.' }
format.json { head :no_content }
end
end
private
# Use callbacks to share common setup or constraints between actions.
def set_post
@post = Post.find(params[:id])
end
# Never trust parameters from the scary internet, only allow the white list through.
def post_params
params.require(:post).permit(:title, :content)
end
end 위의 19번째 줄을 보면(@post = Post.new(post_params)), rails는 parameter를 post_params로 묶어서 처리합니다. 그리고 해당 parameter는 59번 째 줄에서 만들어집니다.
# 59번 째 줄
# Never trust parameters from the scary internet, only allow the white list through.
def post_params
params.require(:post).permit(:title, :content)
end 이와 같은 방식을 strong parameter를 사용한다고 말합니다. 즉, rails는 기존의 사용자가 넘겨준 데이터를 보안상의 이유로 곧이곧대로 믿는 것이 아니라, 사용자가 보내주는 데이터가 우리가 구성한 db에 맞는 데이터가 들어 온 것인지 한 번 더 확인합니다. 그래서, rails는 :title, :content만 form이 받아들이는 데이터로 인식하고 그 이외의 데이터는 저장하지 않습니다. 따라서, DB를 수정할 경우에(table에 새로운 column을 추가하는 경우) 해당 strong parameter도 같이 수정해주어야 합니다.(rails 4에서는 rake db:migrate add_column_to_table ~와 같은 명령어로 자동 수정이 안 됩니다.)
3. DB와 Schema.rb 불일치 문제
마지막으로 migration과 관련된 문제입니다. 이 문제도 strong parameter처럼 오류 메세지를 뿜지 않습니다. 그래서 log쪽에서 확인을 해야하는 문제인데요. rake db:migrate를 통해 만든 db 구성과 schema.rb에 만들어진 db 구성이 다를 때, form 데이터는 저장되지 않습니다.(사실 어떤 데이터든 db에 저장이 안됩니다.)
&nbps;Schema.rb는 db table을 모두 조감하는 하나의 db 밑그림입니다. 처음부터 있는 파일을 아니고 rake db:migrate하면 생기는 db 폴더에 생성됩니다.
# encoding: UTF-8
# This file is auto-generated from the current state of the database. Instead
# of editing this file, please use the migrations feature of Active Record to
# incrementally modify your database, and then regenerate this schema definition.
# Note that this schema.rb definition is the authoritative source for your
# database schema. If you need to create the application database on another
# system, you should be using db:schema:load, not running all the migrations
# from scratch. The latter is a flawed and unsustainable approach (the more migrations
# you'll amass, the slower it'll run and the greater likelihood for issues).
# It's strongly recommended that you check this file into your version control system.
ActiveRecord::Schema.define(version: 20160117164750) do
create_table "posts", force: :cascade do |t|
t.string "title"
t.string "content"
t.datetime "created_at", null: false
t.datetime "updated_at", null: false
end
end 눈여겨 볼 부분은 12번 째 줄에서 # It's strongly recommended that you check this file into your version control system. 에서 볼 수 있듯이 직접 저 파일을 수정해서는 안 된다는 것입니다. 일반적으로 schema.rb와 db table간의 차이는 잘 안 생깁니다. 자주 있는 문제는 아니라는 거죠. 그렇지만, 차이가 생겼을 때는 이를 맞춰주어야 합니다. 이 때는
rake db:schema:dump명령어를 사용합니다. 이 명령어는 현재 우리가 만든 db 구성에 schema.rb 파일을 재구성해주는 명령어입니다.